Category: Business & Reference, Image, English, United States, Maryland
Results
National Archives and Records Administraton The Way We Worked Imagine working in a coal mine. Or in a steel mill. Or at a telephone switchboard. Work and workplaces have gone through enormous transformations between the mid 19th and late 20th centuries. You can view these changes through photographs held by the National Archives and Records Administration. These historical photographs document: The distinctiveness of America's workforce was shaped by many factors—immigration and ethnicity, slavery and racial segregation, wage labor and technology, gender roles, class, as well as ideals of freedom and equality. Most importantly, these images honor those who built this country—the working men and women of America.
Guns, tanks, and bombs were the principal weapons of World War II, but there were other, more subtle forms of warfare as well. Words, posters, and films waged a constant battle for the hearts and minds of the American citizenry just as surely as military weapons engaged the enemy. Persuading the American public became a wartime industry, almost as important as the manufacturing of bullets and planes. The Government launched an aggressive propaganda campaign with clearly articulated goals and strategies to galvanize public support, and it recruited some of the nation's foremost intellectuals, artists, and filmmakers to wage the war on that front.
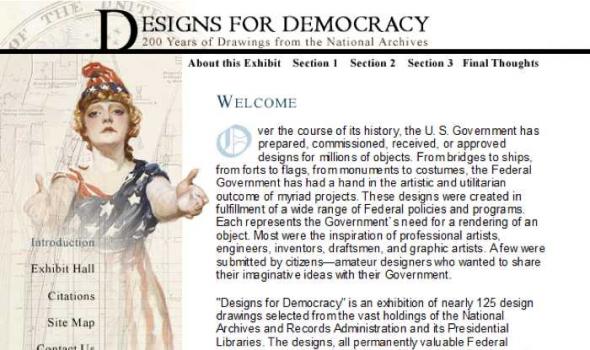
Federal Designs: Symbolism Symbols are an important part of America`s design heritage. They establish and reinforce the national identity and patriotism. In some cases, American symbols are based on recognized associations. The ideals of Greek democracy, the power of Imperial Rome, or the refinements of European fashion frequently are reflected in Federal designs. At other times and for other purposes, designers created icons using images unique to this new country, to this new form of government, and to America`s aspirations to world power.
This on-line version of Here Today, Here Tomorrow... presents a variety of printed medical ephemera from the collections of William H. Helfand and the National Library of Medicine. The exhibit was held at the National Library of Medicine, Bethesda, Maryland, May 22 through September 11, 1995.
History of Medicine America's Tea Craze . . . from a medical standpoint, our preference is emphatically for coffee. Contrast the vigorous, refreshing odor and flavor of a good cup of coffee with the delicate and insipid taste of even a high grade tea; contrast the clear complexion and physical aspect of the individual whose morning meal is a bowl of diluted coffee and who takes his after-dinner cup, with the nervous, emaciated, habitually constipated dyspeptic whose "eye-opener" and "night cap" is tea, and all reason for argument as to our preference ends . JAMA. 1897 Nov 6;29(19):972 , , , , U.S.
History of Medicine Early Days Almanacs have been a part of American life since its very beginning. One of the first books printed in English America was an almanac. By the mid-18th century the almanac had become, after the Bible, the book most likely to be found in ordinary homes. Produced annually, almanacs provided practical information and entertainment. The main feature was a calendar which showed the months and days, the positions of the moon and the planets, religious and civil commemorations, and weather predictions, sometimes decorated with an illustration of a seasonal scene or the sign of the zodiac. Medieval almanacs showed the church’s feast and fast days.
History of Medicine Exhibition Introduction This online exhibit is designed to introduce you to the history of images used in public health posters in the twentieth century. It utilizes the world's largest collection of poster art dealing with questions of health in the United States, housed at the National Library of Medicine. Many of these images can also be viewed through the Images from the History of Medicine (IHM) homepage. The exhibit is divided into two sections that focus on infectious diseases and environmental health concerns, revealing how posters provide an effective medium for communicating information about disease, identifying risk factors, and promoting behavioral change.
History of Medicine Introduction The National Library of Medicine has recently acquired a large collection of Chinese Public Health materials, about seven thousand items produced from early 20th century to the year of SARS. The collection has a wide range of media presentations: posters, health newsletters, health newspapers, paintings, pharmaceutical advertisements, calendars, children's chess games, jigsaw puzzles on health topics, playing cards on SARS, lantern slides, negatives, photographs, and health award certificates, as well as books and journals. These materials present rich visual representations of public health concerns which were closely tied to the political, social, economic, and even military engagements of China during different time periods.
History of Medicine Introduction Malaria was historically a major threat to the health of the Chinese people. In 1950, over 30 million Chinese people suffered from malaria and one percent of them died. The Chinese government launched national campaigns against malaria in the early 1950s. Programs of malaria control were integrated in the general rural development of land reclamation, irrigation construction, and improvement of sanitary conditions for both humans and livestock. While timely treatment of malaria is essential, the anti-malaria campaigns strongly emphasized preventive methods, as "prevention first" was the health policy in the 1950s-1980s.
History of Medicine EVER SINCE THE INVENTION OF moveable type in the mid-1400s, the public’s appetite for tales of shocking murders —“true crime” —has been an enduring aspect of the market for printed material. For more than five centuries, murder pamphlets have been hawked on street corners, town squares, taverns, coffeehouses, news stands, and book shops. Typically, a local printer would put together a pamphlet that claimed to be a true account of a murder, consisting of a narrative, trial transcript, and/or written confession of the murderer before his or her execution. 13 September 2010
History of Medicine Chinese medicinal compounds were recorded as early as the Han dynasty, 2,000 years ago. Beginning in the 1880s, Western companies – notably Bayer, Hoechst (now Aventis), and Eli Lilly – challenged traditional medicine with the resources of modern capitalism. In turn, Chinese companies entered the new commercial markets: the Tianjin Pharmaceutical Factory, founded in 1921, used western methods to produce and market traditional Chinese medicines. The sheets shown here advertise a mix of European and Asian products, using ideal feminine and masculine images as well as the Tian An Men (Gate of Heavenly Peace). Ads for progesterone and methyltestosterone show the appeal of potent over-the-counter hormone therapies. 21 April 2010
History of Medicine Introduction 引言 Tuberculosis was one of the major epidemic diseases in 20th-century China, along with smallpox, malaria, cholera, schistosomiasis, and other epidemics. Organized efforts to fight the disease began in 1933 when the National Anti-Tuberculosis Association of China was established. From 1950 through 1980, the Chinese government launched anti-tuberculosis campaigns as part of the national public health movement. The Anti-TB Association and the Red Cross played important roles in the health education campaigns. Health posters became an important tool to disseminate health knowledge and methods of prevention and treatment. The campaigns, along with the universal free healthcare, led to a significant decline of tuberculosis.
History of Medicine About a hundred years ago, public health took a visual turn. In an era of devastating epidemic and endemic infectious disease, health professionals began to organize coordinated campaigns that sought to mobilize public action through eye-catching wall posters, illustrated pamphlets, motion pictures, and glass slide projections. Impressed by the images of mass media that increasingly saturated the world around them, health campaigners were inspired to present new figures of contagion, and recycle old ones, using modernist aesthetics, graphic manipulations, humor, dramatic lighting, painterly abstraction, distortions of perspective, and other visual strategies.