Category: Science & Technology
Results
Donald Angus Collection of Botanical Prints Donald Angus' collection of botanical prints are housed at the Bishop Museum, Foster Gardens, the National Tropical Botanical Garden, and the University of Hawai'i at Manoa Hamilton Library. These exquisite illustrations were published in monographs and journals mainly in the 18th and 19th centuries. They reflect the enthusiasm of scientists, and the popularity of the exotic flora being introduced and cultivated in European botanical gardens. Many prints in the Angus collection are from Monandrian Plants of the Order Scitamineae by William Roscoe (1753-1831). Roscoe, a wealthy banker and amateur botanist, founded the Liverpool Botanic Garden in 1802.
Japanese American Veterans Collection Chaplain Higuchi Wartime Correspondence During World War II, Hiro Higuchi of Hawaii volunteered to serve as one of two chaplains attached to the 442nd Regimental Combat Team, an all-Japanese American unit formed in January 1943. Following his enlistment, Higuchi attended the U.S. Army Chaplain School at Harvard University in the fall of 1943. In November 1943, he joined the soldiers of the 442nd RCT for intensive training at Camp Shelby, Mississippi. In June 1944, Higuchi accompanied the 442nd RCT to Europe, where he served with the unit in Italy and France. Chaplain Hiro Higuchi returned home to Hawaii in December 1945.
The Valley Project details life in two American communities, one Northern and one Southern, from the time of John Brown's Raid through the era of reconstruction. In this digital archive you may explore thousands of original letters and diaries, newspapers and speeches, census and church records, left by men and women in Augusta County, Virginia, and Franklin County, Pennsylvania. Giving voice to hundreds of individual people, the Valley Project tells forgotten stories of life during the era of the civil war.
Eadweard Muybridge (1830–1904) wished to catalogue every aspect of human and animal locomotion with his camera. He photographed hundreds of subjects engaged in actions both mundane and arcane: nude figures walking and lifting children, athletes boxing and fencing, and animals hurdling, kicking, or slowly ambling along. He was the first photographer to visually dissect these activities, creating images that delighted and mystified the public in the late 19th century.
Cambridge Digital Library Introducing the Cambridge Digital Library Cambridge University Library contains evidence of some of the greatest ideas and discoveries over two millennia. We want to make our collections accessible to anyone, anywhere in the world with an internet connection and a thirst for knowledge." —Anne Jarvis, University Librarian Over the course of six centuries Cambridge University Library's collections have grown from a few dozen volumes into one of the world's great libraries, with an extraordinary accumulation of books, maps, manuscripts and journals. These cover every conceivable aspect of human endeavour, spanning most of the world's cultural traditions.
Peace and War in the 20th Century Welcome The twentieth century has been a century of war. It began with the Boer War in South Africa and ended with the Gulf War in Kuwait and Iraq. This tragic legacy suggests that citizens of the twenty-first century have a shared responsibility to attempt to understand how and why these conflicts occurred and to discover how peace efforts contributed to the resolution of international conflicts. The work of understanding, conscientiously conducted, must draw on primary sources of many kinds, including oral histories, newspapers, contemporary journals, government documents, regimental histories, and archives. Archival resources provide us with a direct link to the past.
2011-2013 Program Review Published annually, the USMA Library Program Review details work of the past academic year and projects forward significant initiatives for the coming academic year. It also provides strategic guidance and awareness for the future of academic information and library support at the U.S. Military Academy.
About Us Read more Founded in 1915, the Cornell Lab is a nonprofit organization supported by 45,000 friends and members . Our vibrant community includes 200,000 citizen-science participants from all walks of life and 5 million bird enthusiasts of all ages who connect with us online at All About Birds. As a proud unit of Cornell University we have ten faculty on staff and access to world-class resources. As a nonprofit environmental organization, however, we depend on members, donors, research, and our other programs for 99 percent of our operating budget. Your support will result in direct impacts and improvements for conservation science. We invite you to join us as a member of the Lab .
The primary mission of Catena, the Digital Archive of Historic Gardens and Landscapes, is to fill a void in American higher education by assembling a searchable collection of historic and contemporary images that include plans, engravings, paintings, and photographs to make the following possible: Provide Images for Teaching Landscape Studies Catena offers a readily available set of images to illustrate classroom lectures.
Led by the State Library of Massachusetts, the Alexander Parris Digital Project digitized Parris material held in the State Library and the collections of six Boston repositories. The Boston Athenaeum; The Boston Public Library; Boston National Historical Park, Charlestown Navy Yard; Massachusetts General Hospital; Massachusetts Historical Society; and Historic New England (formerly Society for the Preservation of New England Antiquities) all contributed documents to a searchable digital archive that contains images and transcriptions of more than four hundred items.
Welcome to the Digital Library for Earth System Education A free service Thank you for your interest in DLESE. This overview is intended to provide you with very general information about DLESE and the library's organization. As always, we welcome your comments and suggestions. Please direct them to support@dlese.org . Browse the Library resources and collections What is DLESE? DLESE is the Digital Library for Earth System Education, a free resource that supports teaching and learning about the Earth system. DLESE's development was funded by the National Science Foundation and continues to be built by a distributed community of educators, students, and scientists to support Earth system education at all levels.
About the Everglades Digital Library The Everglades Digital Library (EDL) is a service of the Digital Collections Center at Florida International University Libraries in Miami, Florida. The EDL was established in 1996 to support research, education, decision making, and information resource management within the greater Everglades community. Since that time, the project has grown to serve patrons from around the world with Web-accessible digital collections, the online reference service 'Ask An Everglades Librarian', and other online information services.
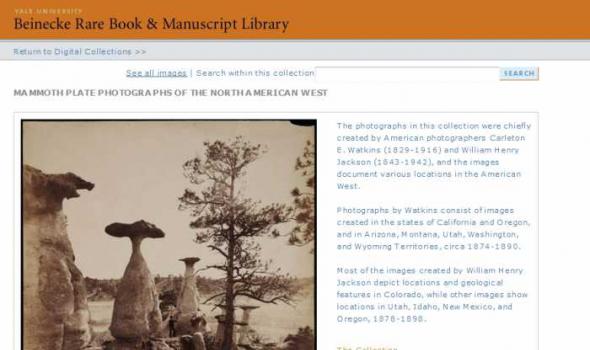
Mammoth plate photographs are photographic prints made through contact printing a photographic print from a large glass plate negative, usually 18 by 21 inches, but may vary in size from 15 by 18 inches to 22 by 25 inches. These large negatives allowed photographers to produce outsized photographic prints before the development of photographic enlargers. The collection consists of 57 black and white photographic prints roughly 21 x 17 inches Cite as: Mammoth Plate Photographs of the North American West. Yale Collection of Western Americana, Beinecke Rare Book and Manuscript Library. Call Number: WA Photos Folio 1
In the autumn of 1609, the Italian mathematician and astronomer Galileo Galilei turned his telescope to the heavens, deciphering the cratered face of the moon, the four satellites of Jupiter, and other previously opaque features of the heavens. When, in 1610, Galileo published his Sidereus Nuncius, or Starry Messenger, the German astronomer Johannes Kepler responded with enthusiasm, praising the significance of Galileo’s observations with his own Dissertatio cum Nuncio Sidereo, or, Conversations with the Starry Messenger (1610). To whom else did the stars speak in the early modern period?
Rachel Louise Carson, noted biologist and environmentalist who fascinated readers with three books on the wonders of the sea and awakened the American public to the dangers of pesticide misuse with a highly controversial bestseller, was born on May 27, 1907, in Springdale, Pennsylvania. She was interested in writing at an early age and submitted a number of juvenile stories, poems, and essays to leading youth magazines. Rachel Carson's first book, Under the Sea Wind , attracted little notice on its appearance in 1941. However, her second book on the sea, The Sea Around Us (1951), remained on the best-seller lists for eighty-six weeks, was eventually translated into thirty languages, and received many awards.
“I have no Knowledge of it at all,” wrote Ezra Stiles of alchemy. “I never saw Transmutation, the aurific Powder, nor the Philosophers Stone,” the early President of Yale College continued, “nor did I ever converse with an Adept knowing him to be such. ...
About From Nylon to Polyethylene, plastics surround us. This website combines narratives about the people, materials, and corporations responsible for our cultural embrace of plastic with a searchable digital collection of original research materials from Syracuse University Library, including manuscripts, printed materials, photographs, and artifacts. Many of these materials are also available to scholars and researchers who visit Syracuse University Library. The Plastics Collection at the Syracuse University Library, founded in 2008, is the largest university-based resource on the history of plastics.
The Erie Railroad Glass Plate Negative Collection Using the Collection The collection of 709 images can be accessed via the Library's CONTENTdm server and is fully searchable by keyword, subject, and image number. The item level inventory of the collection in Excel can help with formulating searches and sorting. NOTE: both links will open new windows. About the Collection The Erie Railroad Company glass plate negatives are arranged by Erie subsidiary railroads in the states of New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, and Ohio. Mainline scenes come from all of the preceding states, as well as from Indiana and Illinois.
This set of 640 images of neurons from the spinal cords thirty-six rats were created for use in Psychology 116, the psychobiology laboratory course, to train students in data analysis and interpretation. This image collection has also been used to test the transfer of digital objects between the Library's digital image collection and course management software systems.
Have questions? Project Title: Idaho Waters Digital Library About the Project: The Idaho Waters Digital Library provides access to information resources relating to water issues in key Idaho river basins. The collection presently includes scientific and technical reports, with an emphasis on Idaho Water Resources Research Institute reports and publications. This centralized digital repository provides a searchable interface for discovery and utilization of water resources documents. As funding sources are identified, this collection will continue to grow in size and scope. Digitized materials from this collection are also available through the Western Waters Digital Library .
A collection of reports, studies, and documents published by the Intermountain Forest Tree Nutrition Cooperative (IFTNC), a research cooperative composed of public and private forestry organizations that is located administratively in the College of Natural Resources at the University of Idaho.