Science
The Mercator Globes Gerard Mercator was a publisher of maps and atlases but he also published two globes — the terrestrial globe of 1541 and the celestial globe of 1551. The globes were an instant commercial success and were the largest (42 cm) that had been produced to date. This online exhibit allows the viewer to study detailed images for each of the globes. The globes are now on permanent exhibit just outside of the entrance to the Map Collection in Pusey Library. Viewing Features of the Exhibition This exhibition offers a unique approach for viewing each globe.
About Enrico Fermi Enrico Fermi (photo courtesy of Argonne National Laboratory) (From the Biographical Note, Guide to the Enrico Fermi Collection, Special Collections Research Center, University of Chicago Library) Enrico Fermi (1901-1954), Charles H. Swift Distinguished Service Professor of Physics at the University of Chicago, and 1938 Nobel Prize winner in physics, is best known to the general public for his leadership of the Manhattan Project team, which succeeded in obtaining the first controlled self-sustaining nuclear chain reaction. This experiment, which was carried out at the University of Chicago on December 2, 1942, made possible the development of the atomic bomb.
From Alchemy to Chemistry: Five Hundred Years of Rare and Interesting Books This website grew out of an exhibit held at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Rare Book Room in April 2000. The Eastern Illinois Section of the American Chemical Society provided support for the construction of this website. The exhibit, "From Alchemy to Chemistry: 500 Years of Rare and Interesting Books," was co-curated by Tina Chrzastowski (Chemistry Librarian), Vera Mainz (Director, VOICE NMR Lab, School of Chemical Sciences), and Gregory Girolami (Professor of Chemistry).
Over the past 300 years or so, Scottish scientists have provided the world with important ideas and inventions. Many of these shape our lives today.
Science is behind many objects we take for granted, such as Alexander Graham Bell's telephone and John Logie Baird's television. It is thanks to scientists like Alexander Fleming that we now have life-saving advances in medicine.
Imagine what life would be like without the work of these, and other, pioneering Scottish scientists.
Editors Stephen Darwall J. David Velleman Editorial Board K. Anthony Appiah | Richard Arneson | Paul Boghossian | Robert Brandom | Michael Bratman | John Broome | Victor Caston | John Cooper | Mark Crimmins | Kit Fine | Daniel Garber | Richard Heck | David Hills | Louis Loeb | Penelope Maddy | Tim Maudlin | Peter Railton | Gideon Rosen | Nancy Sherman | Michael Smith | Robert Stalnaker | Jason Stanley | Jamie Tappenden | Kendall Walton | Stephen Yablo Production and Publication Scholarly Publishing Office, University of Michigan Library Director: Maria Bonn OCLC: 45826937 ISSN: 1533-628X LCCN: 2001-212257 Description Philosophers' Imprint is a refereed series of original papers in philosophy, edited by Stephen Darwall and J.
Overview While theoretical biology is often understood to be primarily mathematical in nature, biology is an inherently historical science with a long tradition of conceptual theorizing, from Charles Darwin to the architects of the Modern Synthesis, and continuing through to today. Biological disciplines ranging from evolutionary biology to ecology, from cell to developmental biology, and from morphology to paleobiology are characterized by a lively interplay among empirical data, mathematical treatments, and conceptual discussions. Like theoretical biology, philosophy of biology is characterized by its attention to conceptual issues.
History of Medicine Robert Hooke (1635-1703) was a remarkably versatile man — artist, biologist, physicist, engineer, architect, inventor, and more. However, his crowning glory was Micrographia: or Some Physiological Descriptions of Minute Bodies made by Magnifying Glasses , first published 1665. It was a masterpiece — an exquisitely illustrated introduction to the previously unknown microscopic world. This exhibit focuses on Hooke's influences and legacy in print, the pioneering books that stimulated Hooke's research, and the works he left for others — most famously the great Dutch microscopist, Antoni van Leeuwenhœk (1632-1723). August 1 – November 1, 2007.
History of Medicine Introduction This Guide to Collections relating to the History of Artificial Organs is a review of materials located in known repositories as well as private and corporate holdings worldwide. This guide is an introduction, not an inventory, to the papers, records, films, tapes, interviews and artifacts relevant to the history of artificial organ developments. Purpose of the Guide This Guide is intended to serve many purposes. It marks an essential first step towards preserving the documentary history of artificial organ developments in the United States and abroad. It is intended to bring attention to the need to preserve recent medical science history before documents and devices are lost.
History of Medicine Introduction This exhibit [and accompanying brochure] highlight the joint observance of the 500th anniversary of the birth of Paracelsus by three American medical libraries -- The Hahnemann University Library, The National Library of Medicine, and The Washington University Medical Library (St. Louis). It has been prepared to accompany the special exhibits which, along with lectures and other programs, are being organized at these libraries. The intent of the various events is to celebrate as well as to explain the contributions of this major Renaissance figure, especially those in medicine, chemistry, and pharmacy.
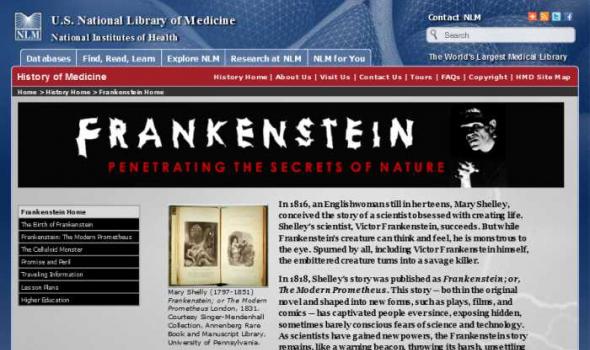
History of Medicine In 1816, an Englishwoman still in her teens, Mary Shelley, conceived the story of a scientist obsessed with creating life. Shelley's scientist, Victor Frankenstein, succeeds. But while Frankenstein's creature can think and feel, he is monstrous to the eye. Spurned by all, including Victor Frankenstein himself, the embittered creature turns into a savage killer. In 1818, Shelley's story was published as Frankenstein; or, The Modern Prometheus . This story — both in the original novel and shaped into new forms, such as plays, films, and comics — has captivated people ever since, exposing hidden, sometimes barely conscious fears of science and technology.
The three sections of It's in the Blood! A Documentary History of Linus Pauling, Hemoglobin and Sickle Cell Anemia work together to provide an unusually rich source of information on Pauling's work in blood biochemistry and molecular disease. Navigate between the sections by using either the links on the site's home page or the links at the top of any page within the site. Narrative - The first section tells the story of Linus Pauling's research into the nature of human blood.
Linus Pauling and The Nature of the Chemical Bond: A Documentary History is comprised of three large sub-sections, each of which tells the story of the elucidation of chemical bond theory in a different way. Navigation between sub-sections may be achieved either through use of the links provided on the site homepage or through use of the links located in the header of each page within the site. Narrative - The first section - a forty-nine "chapter" Narrative - recounts the early years of chemical bond investigation primarily focusing on chemist Linus Pauling’s (1901-1994) research, which he later proclaimed as being his most important contribution to science.
Linus Pauling, an OSU alum (Oregon Agricultural College, class of 1922), was among the most decorated of American scientists. He received his first honorary doctorate from his alma mater in 1933, and in rapid succession was similarly honored by institutions including Oxford University, the University of Chicago, Princeton University, Cambridge University and the Sorbonne. By the time of his death, Pauling had been awarded forty-seven honorary doctorates. Not included in this total is the honorary diploma received in 1962 from Washington High School in Portland, Oregon.
Introduction In 1999, inspired by the remarkable success of the Human Genome Project, the OSU Libraries Special Collections launched an ambitious undertaking that seeks to closely-document virtually every day of Linus and Ava Helen Pauling's lives. The result is Linus Pauling Day-by-Day, a constantly-expanding resource that provides in-depth description for a substantial portion of the half-million item Ava Helen and Linus Pauling Papers. This huge amount of data is presented in easy-to-use calendar form. Index pages created for each year of the Day-by-Day calendar provide an overview of the major events in the Paulings' lives, a full accounting of their travel and snapshots from their various adventures at home and abroad.
Linus Pauling and the Race for DNA: A Documentary History is comprised of three large sub-sections, each of which tells the story of the discovery of the double helix in a different way. Navigation between sub-sections may be achieved either through use of the links provided on the site homepage or through use of the links located in the header of each page within the site. Narrative - The first section - a thirty-four "chapter" Narrative - recounts the saga of the discovery from the largely unknown viewpoint of the major "loser" in the race: the phenomenal American chemist Linus Pauling (1901-1994). There are three components to each page of the Narrative.
The three sections of The Scientific War Work of Linus C. Pauling combine to provide an unusually rich source of information on Linus Pauling's intriguing body of research conducted on behalf of the Allied effort during World War II. Navigate between the sections by using the links on the site's home page or by using the links at the top of any page within the site. Narrative - The first section tells the story of Pauling's work with the National Defense Research Committee, among other important groups, in developing tools meant to benefit the Allied cause in the European and Pacific theatres.
Welcome to the Digital Library for Earth System Education A free service Thank you for your interest in DLESE. This overview is intended to provide you with very general information about DLESE and the library's organization. As always, we welcome your comments and suggestions. Please direct them to support@dlese.org . Browse the Library resources and collections What is DLESE? DLESE is the Digital Library for Earth System Education, a free resource that supports teaching and learning about the Earth system. DLESE's development was funded by the National Science Foundation and continues to be built by a distributed community of educators, students, and scientists to support Earth system education at all levels.
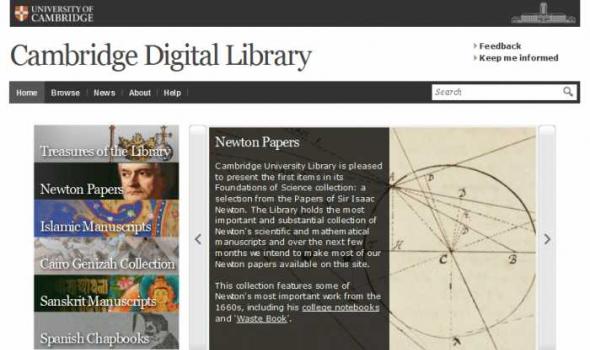
Cambridge Digital Library Introducing the Cambridge Digital Library Cambridge University Library contains evidence of some of the greatest ideas and discoveries over two millennia. We want to make our collections accessible to anyone, anywhere in the world with an internet connection and a thirst for knowledge." —Anne Jarvis, University Librarian Over the course of six centuries Cambridge University Library's collections have grown from a few dozen volumes into one of the world's great libraries, with an extraordinary accumulation of books, maps, manuscripts and journals. These cover every conceivable aspect of human endeavour, spanning most of the world's cultural traditions.